How to operate a drone introduces the exciting world of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). This guide provides a comprehensive overview of drone operation, from pre-flight checks and safety procedures to advanced flight techniques and legal considerations. We’ll explore the fundamentals of drone controls, navigation methods, and flight planning, equipping you with the knowledge to fly safely and responsibly.
Understanding these aspects is crucial for both recreational and professional drone pilots.
We will cover essential topics including pre-flight inspections, understanding various flight modes, navigating using GPS and other methods, planning safe flight routes, performing routine maintenance, and adhering to relevant laws and ethical guidelines. The guide will also delve into advanced techniques such as precise hovering and achieving high-quality aerial photography and videography. By the end, you’ll be well-prepared to take to the skies with confidence.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
A comprehensive pre-flight checklist is crucial for safe and responsible drone operation. It minimizes risks and ensures the drone is in optimal condition for flight. Neglecting this step can lead to accidents and malfunctions.
Pre-Flight Drone Inspection
Before each flight, a thorough inspection of the drone and its components is essential. This involves visually checking the propellers for damage, ensuring the battery is securely connected and adequately charged, verifying the GPS signal strength, and confirming that all sensors and cameras are functioning correctly. Additionally, check the drone’s overall structural integrity for any signs of damage from previous flights.
Drone Safety Regulations and Best Practices
Adhering to safety regulations and best practices is paramount for responsible drone operation. Understanding airspace restrictions, emergency procedures, and operational limitations is critical to prevent accidents and legal issues. These regulations vary by region and are constantly evolving, so staying updated is crucial.
| Regulation | Description | Consequence of Violation | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Airspace Restrictions | Prohibition of drone flights near airports, military bases, and other restricted areas. | Fines, legal action, drone confiscation. | Use flight planning software to identify and avoid restricted airspace. Check local regulations. |
| Maximum Altitude Limits | Limitations on the maximum altitude a drone can reach. | Fines, legal action. | Maintain awareness of altitude restrictions and set appropriate altitude limits within the drone’s flight controller. |
| Visual Line of Sight (VLOS) | Requirement to maintain visual contact with the drone at all times during operation. | Fines, legal action. | Operate the drone within a safe distance and in open areas where VLOS is easily maintained. |
| Emergency Procedures | Having a plan for dealing with unexpected situations, such as loss of control or battery failure. | Damage to property, injury to persons. | Practice emergency landing procedures and understand how to use the drone’s return-to-home function. |
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation
Understanding drone controls and navigation is fundamental to safe and effective operation. This section details the basic controls, flight modes, and navigation methods to help you confidently maneuver your drone.
Basic Drone Controls
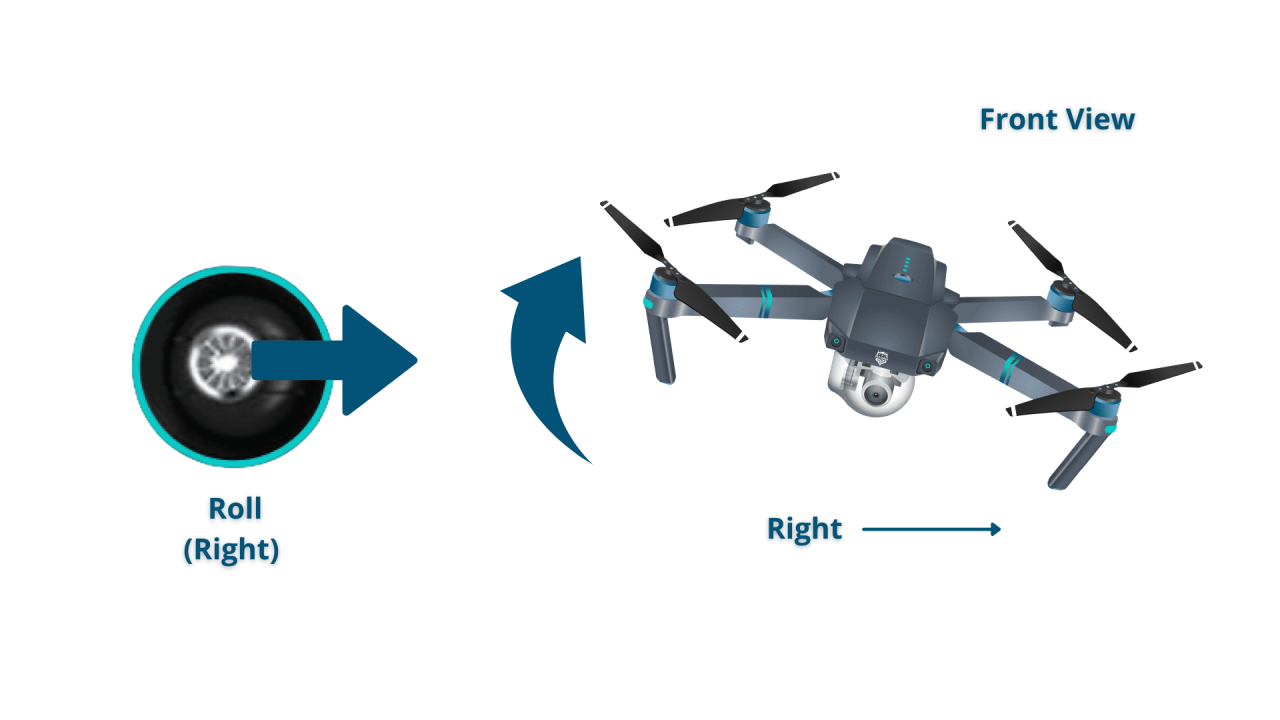
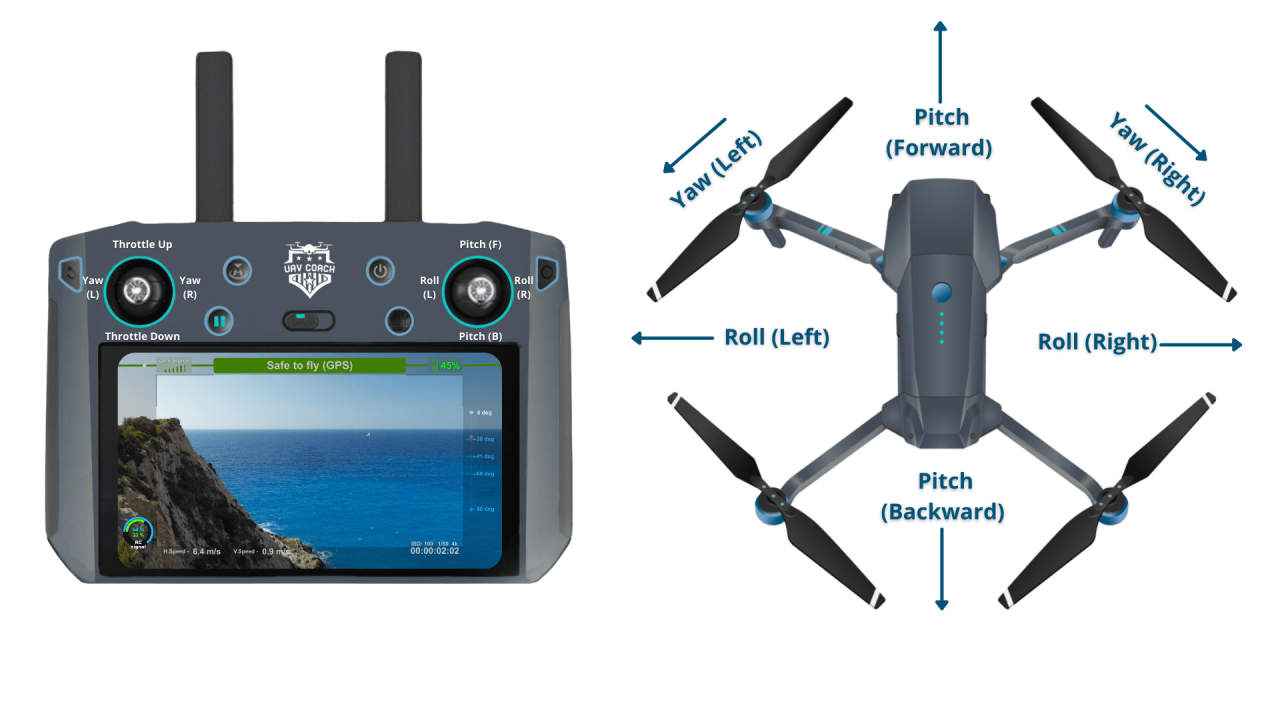
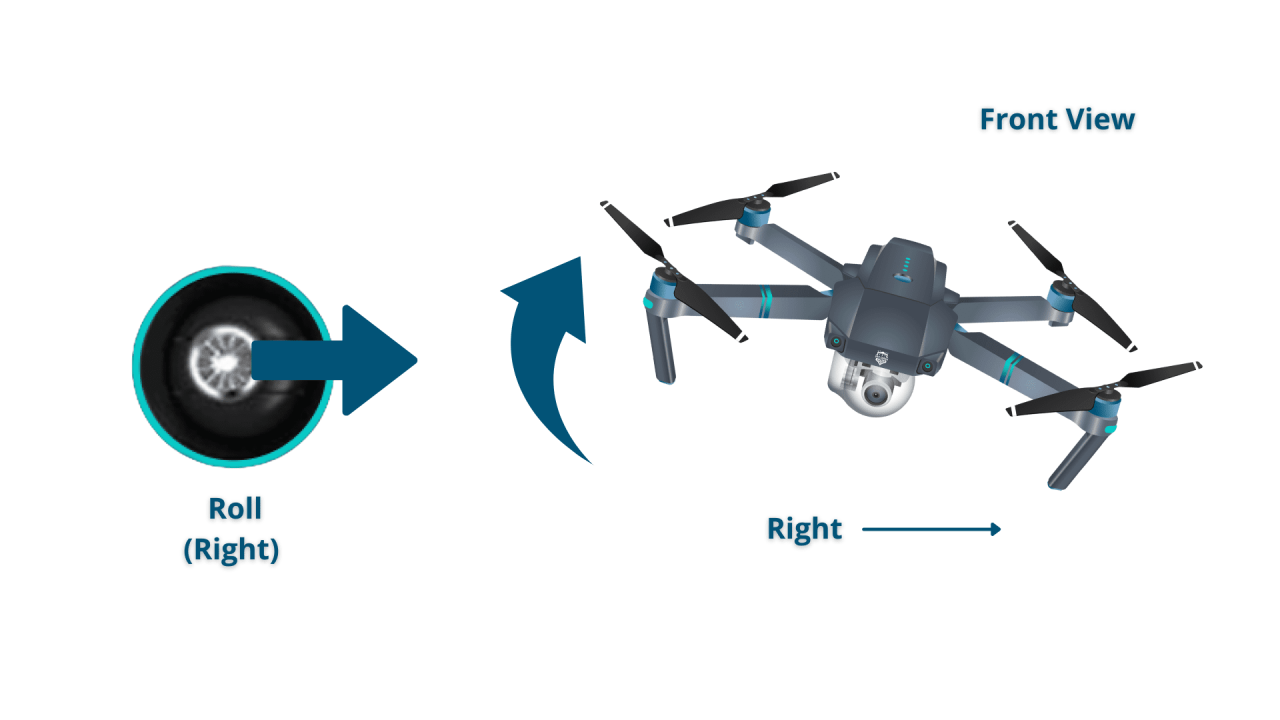
Most drones use a controller with joysticks to control the drone’s movement. The primary controls include throttle (altitude), yaw (rotation), pitch (forward/backward tilt), and roll (left/right tilt). Mastering these controls is essential for basic flight maneuvers. Throttle controls the ascent and descent of the drone, while yaw controls its rotation around its vertical axis. Pitch controls the drone’s movement forward and backward, and roll controls its movement left and right.
Flight Modes and Functionalities
Many drones offer various flight modes, each designed for different skill levels and situations. Beginner mode typically limits speed and responsiveness, making it easier for novices to control the drone. Sport mode increases speed and responsiveness, allowing for more dynamic maneuvers. Other modes may include GPS mode for autonomous flight, and follow-me mode which allows the drone to automatically track a subject.
The specific flight modes and their functionalities vary depending on the drone model.
Drone Navigation Methods
Drones utilize various navigation methods for positioning and movement. GPS uses satellite signals for precise positioning, allowing for autonomous flight and return-to-home functionality. Visual positioning relies on camera sensors to identify and track features in the environment for accurate location and movement. Manual control provides direct control over the drone’s movements using the controller joysticks.
Step-by-Step Guide for Beginner Drone Control
- Familiarize yourself with the controller and its functions.
- Practice hovering the drone at a low altitude in a safe, open area.
- Gradually increase altitude and practice maintaining a stable hover.
- Practice moving the drone forward, backward, left, and right in small, controlled increments.
- Practice rotating the drone using the yaw control.
- Once comfortable with basic maneuvers, try more complex movements, such as figure-eights and slow ascents and descents.
Flight Planning and Mission Execution

Careful flight planning is essential for safe and efficient drone operations, especially for complex missions. This involves identifying safe flight zones, considering environmental factors, and creating a detailed flight plan. This section provides guidance on flight planning and executing various drone missions.
Importance of Flight Planning, How to operate a drone
Flight planning minimizes risks by identifying potential hazards, such as obstacles, restricted airspace, and weather conditions. It ensures the drone operates within legal and ethical boundaries, maximizing the chances of a successful mission while minimizing the risk of accidents or violations. A well-defined flight plan Artikels the intended flight path, altitude settings, and other relevant parameters.
Creating a Flight Plan
Creating a flight plan typically involves identifying waypoints (locations the drone will fly to) and setting appropriate altitude settings for each waypoint. Flight planning software can help visualize the flight path and ensure it avoids restricted airspace and obstacles. Consider factors like wind speed, visibility, and potential hazards when designing the flight plan.
Drone Missions and Flight Parameters
Different drone missions require specific flight parameters. Aerial photography might involve slow, steady movements to capture detailed images. Videography might require smoother, more dynamic movements to create engaging footage. Inspection missions may necessitate precise movements to capture close-up images of specific areas. Each mission requires careful consideration of factors such as camera settings, flight speed, and altitude.
Executing a Complex Drone Mission
- Review the flight plan thoroughly to ensure accuracy and safety.
- Conduct a pre-flight check of the drone and its components.
- Obtain necessary permissions and licenses if required.
- Begin the mission, following the planned waypoints and altitude settings.
- Monitor the drone’s status and battery level throughout the flight.
- Execute emergency procedures if necessary.
- Land the drone safely once the mission is complete.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance is crucial for keeping your drone in optimal condition and preventing malfunctions. This section Artikels routine maintenance tasks, common malfunctions, and troubleshooting steps.
Regular Drone Maintenance Tasks

Regular maintenance involves tasks such as cleaning the drone’s body and propellers, inspecting for damage, lubricating moving parts, calibrating sensors, and updating the firmware. The frequency of these tasks depends on the drone’s usage and environmental conditions. A clean and well-maintained drone is less prone to malfunctions and will have a longer lifespan.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Troubleshooting
Common malfunctions include motor issues, GPS signal loss, battery problems, and camera malfunctions. Troubleshooting steps often involve checking connections, replacing faulty components, recalibrating sensors, or updating the firmware. Consulting the drone’s manual is essential for specific troubleshooting procedures.
Battery Care and Charging Procedures
Proper battery care is crucial for extending battery life and ensuring safe operation. Avoid overcharging or discharging the batteries, and store them in a cool, dry place when not in use. Always use the manufacturer-recommended charger and follow the charging instructions carefully.
Routine Drone Maintenance Checklist
- Inspect propellers for damage.
- Clean the drone body and propellers.
- Check battery levels and charging status.
- Calibrate the compass and IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit).
- Check for loose screws or connections.
- Update firmware to the latest version.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Operating a drone involves legal and ethical responsibilities. Understanding these considerations is crucial for responsible drone use. This section covers legal regulations, ethical considerations, and the process of obtaining necessary permits and licenses.
Legal Regulations and Airspace Restrictions
Drone regulations vary significantly by region. Many countries and regions have specific rules regarding airspace restrictions, registration requirements, and operational limitations. It’s crucial to research and comply with the specific regulations in your area before flying. Failure to comply can result in fines, legal action, or even criminal charges.
Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations involve respecting privacy, avoiding reckless operation, and ensuring responsible use of the drone’s capabilities. Always obtain consent before filming or photographing people or private property. Avoid flying in areas where your drone might disturb wildlife or cause other disruptions. Responsible drone operation is about balancing the benefits of drone technology with the need to protect individuals’ privacy and safety.
Obtaining Necessary Permits and Licenses
Depending on the location and intended use, you might need permits or licenses to operate a drone. These permits often require demonstrating competence and understanding of safety regulations. Check with your local aviation authority to determine the specific requirements in your area.
Decision-Making Process for Legal and Ethical Drone Operation
A flowchart can visually represent the decision-making process for determining the legality and ethical permissibility of a specific drone operation. The flowchart would involve a series of yes/no questions about location, purpose, and potential impact on privacy and safety, ultimately leading to a decision about whether the operation is acceptable.
Advanced Drone Techniques
This section explores advanced flight maneuvers, drone features, and techniques for achieving high-quality aerial photography and videography.
Advanced Flight Maneuvers
Advanced maneuvers such as precise hovering, smooth transitions, and complex camera movements require significant practice and skill. These techniques enhance the quality of aerial footage and allow for more creative shots. Mastering these maneuvers requires understanding the drone’s responsiveness and developing a good sense of spatial awareness.
Advanced Drone Features
Modern drones often include advanced features like obstacle avoidance, which automatically detects and avoids obstacles, and return-to-home functionality, which allows the drone to automatically return to its starting point in case of signal loss or other emergencies. These features enhance safety and simplify operation.
Understanding drone operation involves familiarizing yourself with its controls and safety protocols. Successfully navigating the skies requires practice and understanding of airspace regulations. For a comprehensive guide on the intricacies involved, consult this helpful resource on how to operate a drone before your first flight. This will ensure you’re well-prepared to handle your drone responsibly and safely.
Achieving High-Quality Aerial Photography and Videography
High-quality aerial footage requires careful attention to camera settings, composition, and lighting. Understanding the impact of aperture, shutter speed, and ISO on image quality is crucial. Proper composition involves framing the shot effectively and using leading lines and other compositional techniques to create visually appealing images.
Successfully operating a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is available at how to operate a drone. This website provides comprehensive guidance on everything from pre-flight checks to navigating complex maneuvers, ensuring a safe and efficient drone operation experience.
Drone Camera Settings and Image Quality
Different camera settings affect the final image or video quality. Aperture controls depth of field, shutter speed controls motion blur, and ISO controls image sensitivity to light. Understanding how these settings interact and their impact on the final product is essential for achieving desired results.
Drone Photography and Videography
This section focuses on optimizing drone settings and techniques for capturing high-quality aerial photography and videography.
Setting Up a Drone for Optimal Image Capture
Before taking flight, ensure the drone’s camera is properly calibrated and that all settings are optimized for the desired shot. This might involve adjusting the camera’s field of view, white balance, and other settings to achieve the desired look and feel.
Adjusting Camera Settings
Adjusting camera settings such as aperture, shutter speed, and ISO is crucial for achieving the desired results. Aperture affects depth of field, shutter speed controls motion blur, and ISO affects image noise. Understanding the interplay of these settings is key to capturing high-quality images and videos.
Tips for Composing Compelling Aerial Shots and Videos
Composing compelling aerial shots involves considering factors such as lighting, perspective, and subject placement. Using leading lines, rule of thirds, and other compositional techniques can enhance the visual appeal of your shots. Experiment with different angles and perspectives to find the most effective way to showcase your subject.
Comparison of Drone Camera Features
| Camera Feature | Suitability for Landscape Photography | Suitability for Action Videos | Suitability for Inspection |
|---|---|---|---|
| High Resolution Sensor | Excellent | Good | Good |
| Wide Field of View | Good | Excellent | Good |
| High Frame Rate | Not Applicable | Excellent | Good |
| Zoom Capability | Good | Good | Excellent |
Mastering the art of drone operation is a rewarding journey that combines technical skill with responsible decision-making. From understanding basic controls to executing complex missions, this guide has provided a structured path to proficiency. Remember, consistent practice, adherence to safety regulations, and continuous learning are key to becoming a skilled and ethical drone pilot. Embrace the technology responsibly, and enjoy the breathtaking perspectives that drone flight offers.
FAQ Resource: How To Operate A Drone
What type of drone is best for beginners?
For beginners, a user-friendly drone with GPS, automatic return-to-home functionality, and beginner flight modes is recommended. Look for models known for their stability and ease of control.
How long does it take to learn to fly a drone?
The time it takes to learn varies depending on individual aptitude and practice. Consistent practice with a simulator and real-world flights under safe conditions is key. Expect to spend several hours to gain proficiency.
What is the range of a typical drone?
Drone range varies greatly depending on the model and environmental conditions. Check the manufacturer’s specifications for the specific range of your drone. Keep in mind that factors like signal interference and battery life can significantly affect the actual range.
What happens if my drone loses its signal?
Most modern drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function that automatically guides the drone back to its starting point if the signal is lost. However, always fly within visual line of sight and be prepared for unexpected events.